The digital revolution: LLMO, GEO and SEO in the AI Search optimization
The digital landscape is undergoing an unprecedented transformation, driven by the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) at the heart of search engines and content generation.
This profound reconfiguration is redefining how users find and consume information, transcending traditional search engine results pages (SERPs).
The AI Search Revolution
From clicks to citations: Navigating the new digital frontier of SEO, LLMO, and GEO.
in 2024 alone, signaling a massive shift driven by AI.
with AI-generated summaries by Feb 2025, fueling the rise of “zero-click search.”
Deconstructing the disciplines
The old rules of search are evolving. Understand the three core pillars of modern digital visibility and their unique objectives.
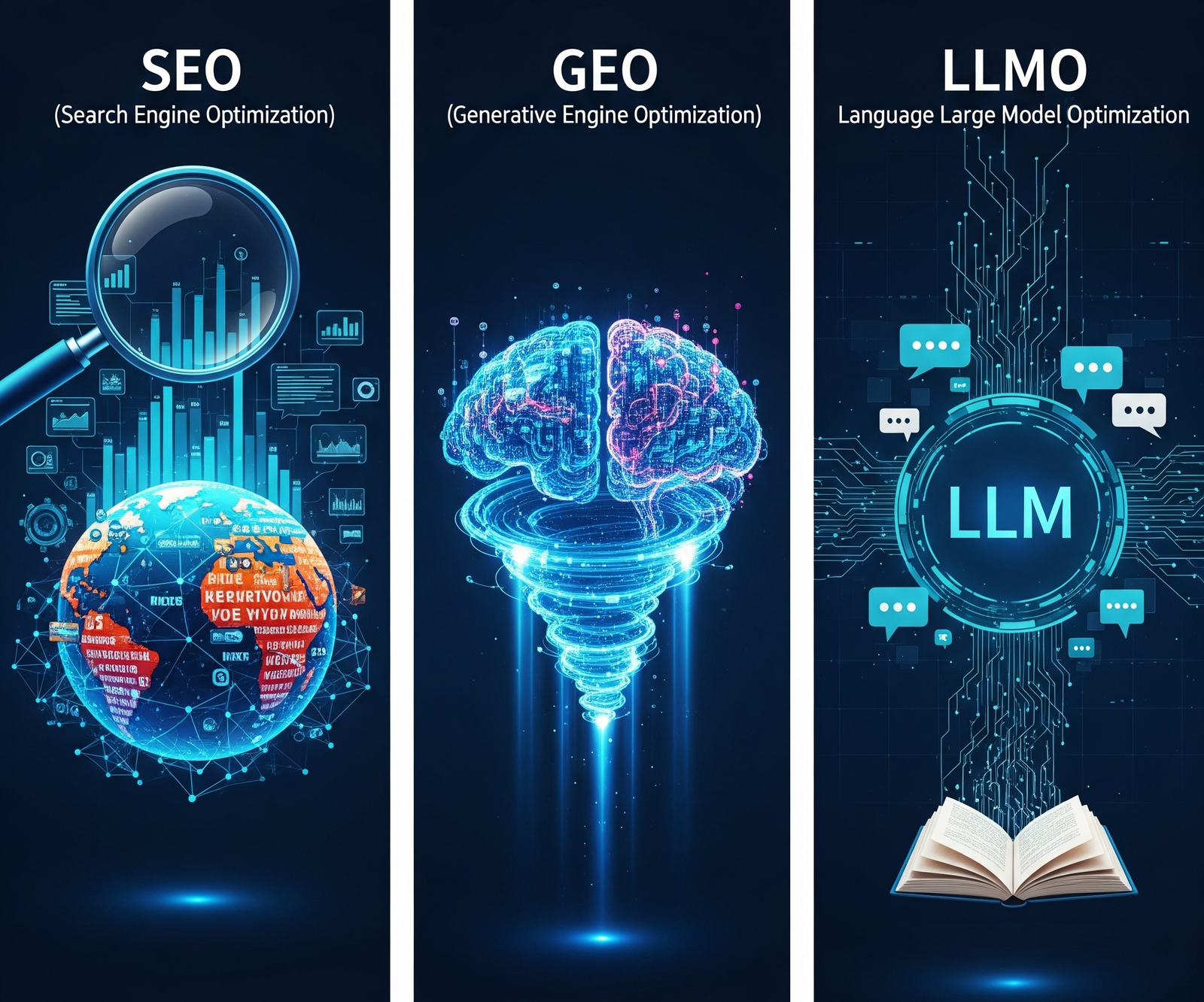
SEO: The Foundation
Goal: To rank high in traditional search results (SERPs) to drive organic clicks and traffic to your website. It’s about being found through crawling, indexing, and ranking.
LLMO: The Interpreter
Goal: To be correctly understood, interpreted, and used as a credible source by Large Language Models (like ChatGPT). The focus is on semantic clarity and structure for AI comprehension.
GEO: The Answer
Goal: To be directly cited and featured in the answers of Generative Engines (like Google’s AI Overviews). It’s about becoming the authoritative source for AI-synthesized responses.
SEO vs. LLMO vs. GEO: A Comparative View
While they share a common foundation of quality content, their goals, metrics, and technical nuances are fundamentally different.
| Characteristic | SEO | LLMO | GEO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Drive traffic via clicks | Ensure AI comprehension | Be cited in AI answers |
| Success metric | Rankings, organic traffic | AI-perceived authority | Citation frequency, visibility Score |
| Key authority signal | Quality backlinks | Unlinked brand mentions | Cited sources & EEAT |
| Technical focus | Crawling, page speed, mobile | No-JS crawlability, structure | Easy data extraction, schema |
Fueling the generative engine
Certain content strategies have a disproportionately large impact on your visibility in AI-generated responses. Prioritizing verifiable, data-backed, and authoritative information is key.
The synergy flow: An integrated strategy
These disciplines aren’t silos; they form a powerful, cyclical strategy. Strong SEO provides the data for LLMs, and GEO success refines your entire approach.
1. SEO Foundation
Builds visibility & crawlability
2. LLMO Optimization
Creates structured, clear content
3. GEO Visibility
Achieves citations in AI answers
Feedback Loop: Insights from GEO performance inform and refine the entire SEO & LLMO strategy.
Your Action Plan for the AI Era
Adapt your strategy with these key takeaways to not only survive but thrive in the new age of search.
Prioritize quality & Depth
Invest in comprehensive, accurate, data-driven content with expert citations and real-world examples.
Optimize for AI
Use Q&A formats, lists, tables, and structured data (Schema) to make your content easily digestible for algorithms.
Focus on EEAT and generating brand mentions in reliable sources, not just traditional backlinks.
Monitor & Adapt
Actively track your visibility in both traditional and generative results, and be ready to adapt your strategy continuously.
AI has become a fundamental component of the online experience in 2025, exerting considerable influence in all areas, from social media to search engines.
Google alone, for example, implemented approximately 5249 algorithm updates during 2024, highlighting “AI Overviews” and “zero-click search” as the most significant.
This astonishing number of algorithmic updates and the prominence of “AI Overviews” demonstrate that AI is not a mere passing trend, but the central engine of search evolution.
This represents a fundamental restructuring in how online information is accessed and consumed. Companies that consider AI integration optional or a niche concern risk falling behind.
Adaptability and continuous learning in AI-driven optimization are no longer just competitive advantages, but essential requirements for survival in today’s digital environment.
Traditional SEO focused on ranking a website to get a click and drive direct traffic.
However, with “AI Overviews” and generative responses, users receive synthesized information directly in the search interface, often without needing to visit the source website.
This phenomenon, known as “zero-click search,” implies a fundamental shift in user behavior: they are less likely to click on a website if their query is answered directly on the SERP.
As a result, success metrics for digital visibility are evolving. While clicks remain important, metrics such as “citation frequency,” “AI visibility score,” and “zero-click value” are becoming equally, if not more, critical.
This demands a profound re-evaluation of content strategy, shifting from generating traffic to becoming a reliable and authoritative source for AI.
This report aims to demystify the concepts of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization), and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), offering a comprehensive guide to navigating this constantly evolving ecosystem.
We will explore their definitions, fundamental differences, and, crucially, how they can be integrated into a cohesive strategy to ensure a sustainable and successful digital presence in the AI era.
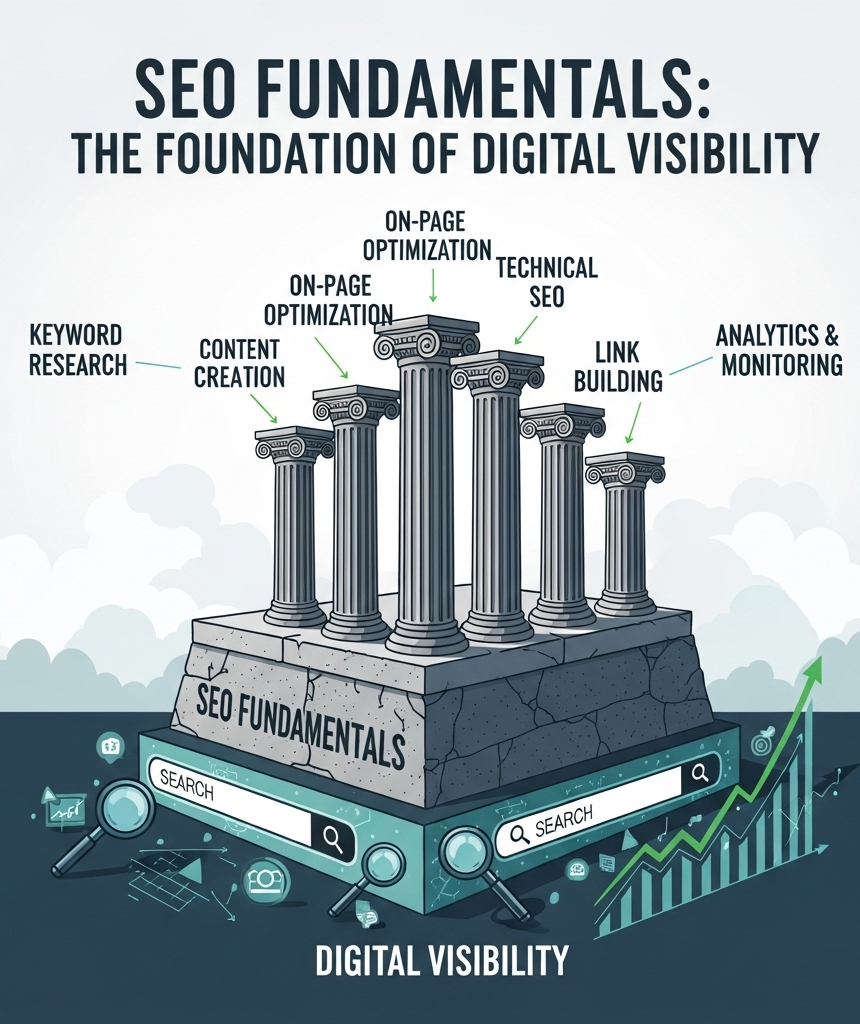
1. SEO fundamentals: The foundation of digital visibility
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the strategic process designed to improve a website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google and Bing
Its primary goal is to increase organic traffic and a brand’s online presence, aiming for a site to be easily found by users interested in its content, without resorting to paid advertising.
This process involves researching search queries, creating useful content, and optimizing the user experience to improve organic search rankings.
How search engines work
Search engines operate through a cycle of three interconnected phases to discover, organize, and present web content:
Crawling
Search engines use software programs, known as “bots” or “web spiders,” to thoroughly explore the internet for new or updated pages. These bots follow links from one page to another to discover new content. For a page to be discovered by these bots, it is essential that at least one link points to it.
This process is the gateway for any content to be considered by the search engine.
Indexing
Once content has been crawled, it is meticulously analyzed to understand its topic, keywords, structure, and relevance. All this information is processed and stored in the Google Index, a gigantic database containing billions of web pages.
Indexing is crucial because only indexed content can appear in search results.
Ranking
When a user enters a search query, the search engine evaluates the indexed content, applying a set of over 200 ranking factors. This complex algorithm determines which pages are most relevant and of the highest quality for that specific query, and positions them on the SERP in a determined order.
The search engine’s goal is to provide the best services to its visitors, delivering high-quality and relevant results for what the searcher is looking for.
Key SEO components
SEO is articulated into several fundamental categories that, together, aim to optimize a website’s online presence:
On-Page SEO
This category covers all optimization elements that are directly controlled within the website itself. Its objective is to make the page’s content and structure more appealing to search engines and users.
- Content: Creating useful, relevant, high-quality, informative, and constantly updated content is paramount. Content should be designed to satisfy user search intent, which is the underlying reason for a specific query.
- Keywords: Involves thorough research to identify terms the target audience uses and their strategic use in content. It is crucial to avoid harmful practices like “keyword stuffing,” which is the overuse of terms and can lead to penalties from search engines.Keyword relevance is fundamental to satisfying user search intent.
- Meta tags: Title tags and meta descriptions are essential elements that communicate a URL’s purpose and expand on the title in search results, respectively. These appear in SERPs and are the first impression users have of the content.
- Content structure: Logical organization of content through proper use of headings (H1, H2, etc.) not only facilitates reading for users but also improves topic comprehension for search engines.A clear structure helps AI identify text portions that answer a query.
- User experience (UX): Intuitive navigation, fast loading speed (measured by Core Web Vitals, such as Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift), and a responsive design that adapts to mobile devices are critical factors for ranking and user retention. Search engines aim to provide the best possible experience to their users, and a user-friendly, fast website is a key indicator of quality.
- Structured data (Schema markup): Implementing schema markup (like FAQPage, HowTo, Product, Article schema) helps search engines understand content context and meaning more deeply. This can improve how content is presented in search results, often in rich formats like featured snippets.
Off-Page SEO
This category refers to actions performed outside the website to improve its ranking and authority in the digital ecosystem.
- Backlinks: Links from other high-authority and relevant web pages act as “votes of confidence” for the site. The quality of these links is vital; low-quality links or “black hat SEO” tactics can be detrimental and lead to penalties. Backlinks are fundamental to SEO because they indicate to search engines that the content is valuable and relevant.
- Brand mentions: References to the brand on other websites, online directories, or social media platforms contribute to its reputation and visibility. These mentions, even without a direct link, can signal a brand’s relevance and existence to search engines.
- Content marketing and social media: Strategic promotion of content on various platforms can generate visibility, attract links, and foster audience interaction, which in turn can improve ranking.
Technical SEO
Focuses on the underlying infrastructure of the website to ensure its efficient accessibility and crawlability by search engines.
- Domain and URL Structure: A logical, user- and search-engine-friendly URL structure is important for site organization and content comprehension.
- Robots.txt and XML Sitemaps: These files guide search engine crawlers, telling them which parts of the site they should or should not crawl and index, and providing a “map” of all important URLs on the site.
- HTTPS Protocol: Website security through HTTPS is an important ranking factor, as Google prioritizes secure sites.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensuring the website is fully functional and easy to use on mobile devices is crucial, given the prevalence of mobile browsing. This includes a responsive design that adapts to any screen size.
- Website Accessibility: Implementing accessibility improvements, such as alternative text for images and design considerations, to make the site usable by people with diverse abilities. This not only improves the experience for all users but can also help search engines better understand visual content.
Importance of SEO
SEO is fundamental for multiple reasons: it allows businesses to reach their target market, connect with consumers and business buyers at all stages of the sales funnel, educate users to make informed decisions, invest in a cost-effective marketing strategy, improve traffic quality, increase lead generation, and ultimately, generate revenue.
Good SEO should ensure amplified reach, drive qualified traffic, and enhance user trust.
Search intent
Understanding the underlying reason why a user performs a specific query is a pillar of modern SEO. Search engines aim to satisfy this intent. Four main types of search intent are identified:
- Navigational: The user is looking for a specific website or location (e.g., “Spotify login”).
- Informational: The user is looking for information about a topic (e.g., “what is Spotify”).
- Commercial: The user is researching before a potential purchase (e.g., “Spotify review”).
- Transactional: The user intends to make a purchase or a specific action (e.g., “Spotify premium”).
Long-Term nature of SEO
SEO is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix; results, while powerful, are often not immediate and require a constant investment of time and effort.
Its essence is not about “tricking” Google with tricks or “hacks,” but about convincing it to rank a page by demonstrating the genuine value it brings to users.
Optimization is a continuous process; even when reaching the top spot, competition never rests, requiring constant improvement.
SEO functions as an interconnected ecosystem, not as a list of isolated tasks. Dividing SEO into categories like On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical, while useful for organization, might suggest distinct silos. However, the consistent emphasis on “content quality,” “user experience,” “relevance,” and “authority” across all categories reveals a holistic system.
For example, technical SEO, by improving loading speed and mobile adaptability, directly impacts user experience, which in turn influences engagement metrics Google considers for ranking. Similarly, high-quality content naturally attracts backlinks, boosting off-page authority.
A truly effective SEO strategy requires a synergistic approach where improvements in one area positively impact others. Neglecting one aspect can undermine efforts in others, underscoring the need for a holistic view to understand how traditional SEO principles translate and remain relevant in the AI-driven landscape.
Furthermore, the definition of “relevance” and “quality” in SEO has evolved significantly. Initially, SEO was heavily influenced by keyword frequency.
However, current research consistently highlights a shift towards “content quality,” “relevance to user intent,” and “semantic understanding.”The mention of “over 200 factors” for ranking indicates a complex and nuanced algorithm that goes beyond simple keyword matching to achieve a deeper understanding of natural language and user needs.
This paves the way for the emergence of LLMO and GEO, which inherently demand this deeper level of content quality and semantic understanding. Content creators must prioritize genuine value, comprehensive answers, and natural language over mere keyword density, as the “human-first” approach to content, even for machines, is becoming paramount.
2. LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization): Optimizing for AI comprehension
LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization), also known as LLM SEO, refers to the process of preparing and refining website content so that large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, can understand it, use it as a reference, and present it in their automatically generated responses.
Its primary goal is not to achieve ranking in traditional search engines, but for the content to be interpreted, cited, and recognized as a reliable source by Artificial Intelligence.
Why LLMO is crucial in the current era
The importance of LLMO lies in the evolution of user behavior and the growing influence of AI in how information is consumed:
- Increase in conversational search and “Zero-click search”: A growing number of users obtain answers directly from these AI models without needing to visit websites. User satisfaction with AI-generated summaries has seen a notable increase, from 37.4% in June 2024 to 75.1% in February 2025, underscored by the preference for direct answers. This shift in search behavior makes it essential for content to be accessible and understandable to LLMs.
- Real authority and competitive advantage: Being cited by an AI not only confers significant visibility but also establishes a brand as an authoritative and credible reference in its sector. This generates a perceived authority that goes beyond traditional ranking. Since most companies are not yet specifically optimizing for AI, adopting LLMO now represents a significant competitive advantage, allowing them to gain ground before the rest of the market adapts.
- New sources of traffic and visibility: LLMs have the potential to become a new and valuable source of organic traffic, expanding a brand’s visibility beyond traditional search channels. Even if a direct click is not generated, the brand’s mention in an AI response can increase user recognition and trust, which can lead to future interactions.
LLMO optimization principles for content
Optimization for language models focuses on content quality, structure, and authority, allowing AI to process and use it effectively:
- Semantic and contextual clarity: LLMs prioritize content that directly aligns with the user’s question and value contextual integrity, ensuring that each segment of text maintains thematic coherence.
This means content must be clear, concise, and unambiguous, directly answering user intent. The focus shifts from simple keyword matching to a deep and nuanced understanding of the topic, its entities, and the relationships between them. This aligns with the evolution of traditional SEO towards semantic SEO. - Content Structure for AI: A logical and predictable structure facilitates information extraction by LLMs.
- Question-answer and FAQ format: Structuring content in a question-answer format, using clear interrogative headings and Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) sections, makes it easier for LLMs to identify and extract direct answers.
- Concise language and logical structure: It is essential to avoid overly complicated language, “keyword stuffing,” and unnecessary jargon. Using a conversational and natural tone, similar to everyday conversation, is recommended, which not only helps the model process the content but also makes it more appealing to readers.
- Executive summaries and TL;DR (Too long; didn’t read): Including concise summaries at the beginning of the content helps models quickly grasp the essence of the text, which is especially useful for extensive content.
- Lists and tables: AI-generated results with a higher success rate are often presented in simple, easy-to-understand formats, such as tables and lists. This facilitates the extraction of key points by the models.
- Informational depth and AI-perceived authority: The quality and credibility of content are fundamental for an LLM to consider it a reliable source.
- Comprehensive and In-depth content: It is crucial to create complete and detailed content that goes beyond superficial information, offering rich context and concrete practical knowledge. LLMs seek information that is useful for answering a query comprehensively.
- Citations and statistics: Including expert citations, statistics, data, and real-world examples reinforces the credibility and authoritative nature of the content. Statistics, for example, can increase visibility in generative responses by 65.5%, and adding expert citations can boost visibility by 41%.
- Authorship and credibility (EEAT): Clearly signing content to identify the author and linking to other relevant content (own or external) with discernment are practices that strengthen credibility and perceived expertise.LLMs tend to extract information from domains they perceive as highly authoritative.
This is distinct from traditional SEO’s reliance on backlinks for authority (PageRank). While backlinks are still important for SEO, direct mentions and perceived expertise become critical for LLMs.
Building brand authority and establishing oneself as an expert in a niche becomes paramount for LLMO.
This involves not only creating great content but also engaging in digital public relations to gain mentions from reliable sources, ensuring NAP (Name, Address, Phone) citation consistency, and leveraging structured data to signal expertise.
The goal is to become an “entity” that AI recognizes as authoritative within a given domain.
- Freshness and constant information updates: LLMs value current information. It is imperative that content is kept updated, incorporating current statistics and trends, and removing any outdated information that might detract from its value. This ensures the model has access to the most relevant and accurate data.
- Entity optimization and data consistency: It is fundamental to clearly identify and define key entities within the content and maintain consistent references throughout the text. Connecting the brand with as many related queries as possible increases its relevance and the likelihood of appearing in AI responses.
- Specific technical considerations for LLMs: It is important to note that most popular AI crawlers (such as those used by OpenAI and Anthropic) do not render JavaScript. This implies that content dynamically loaded via JavaScript might not be visible to them.
Websites that heavily rely on client-side rendering for core content may face significant visibility issues with LLMs.
This requires a re-evaluation of web development practices to ensure critical content is available in the initial HTML load or through server-side rendering, making it accessible to all types of crawlers.
The emergence of specific crawling rules for LLMs (likellms.txt) is anticipated to guide these tools through content and facilitate quick access and analysis.
Concrete benefits of LLMO
Implementing LLMO can lead to increased brand visibility, enhanced perceived authority, the opening of new traffic sources, and significant differentiation from the competition.
By being recognized and cited by LLMs, a brand not only gains exposure but also positions itself as a reference in its industry, which can lead to increased brand recognition and, ultimately, conversions.
3. GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): Ranking in generative search engines
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is a contemporary digital strategy designed to enhance content visibility and influence within responses generated by AI-powered platforms, such as ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, and Google’s “AI Overviews”.
Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on improving rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs), GEO concentrates on ensuring that content is recognized and utilized by large language models (LLMs) when formulating answers to user queries.
The Paradigm Shift from Traditional SERPs to Synthesized Responses
Generative search engines are not limited to cataloging and ranking websites; their primary function is to produce direct answers and solutions to queries, often presented as concise summaries or detailed analyses.
This evolution means users no longer need to click on multiple links to find the information they seek; they receive it directly in the search interface, known as “zero-click search”.
This new dynamic is driving a revolution in strategic web considerations. Brand visibility now occurs “off-site”, which requires content creators to develop specific strategies for their material to be considered authoritative and relevant enough to be included in these AI-generated responses.
The “answer engine” paradigm and its implications for Return on Investment (ROI) are profound. GEO explicitly aims to be “cited in AI-generated responses”, moving away from the goal of generating direct website clicks.
This implies a fundamental shift in the immediate user journey and, consequently, in how ROI is measured. If users get the answer directly, the traditional “click-through rate” loses some of its primacy. Instead, “citation frequency,” “AI visibility score,” and “zero-click value” become key metrics.
Marketers must redefine success beyond direct website traffic. Brand notoriety, authority building, and becoming a “primary reference” within AI responses become direct goals.
This could lead to a longer, more complex conversion funnel, where the initial interaction is with AI, and the website visit (or conversion) occurs later, driven by brand recognition established through AI citations.
This also means adapting content for “conversion” even without a direct click, such as adding to cart within Google Shopping via an AI overview.
Key Strategies for GEO Optimization
To ensure content is cited and used by generative engines, specific strategies must be implemented:
- Content accuracy and comprehensiveness: Clearly articulated and comprehensive content significantly increases the likelihood of being selected as a reference by AIs.AI prefers content that is unambiguous and directly answers user intent. Clarity, conciseness, and directness of content are valued by AI, which seeks direct and unambiguous answers.
- Strategic inclusion of expert citations and statistics: Generative AIs place extremely high value on verifiable and data-backed information.
- The incorporation of citations from relevant sources and statistical data has shown a remarkable increase in source visibility, exceeding 40% across various queries.
- Referencing reliable and pertinent sources can boost content presence in AI-generated responses by an impressive 132.4%.
- Including statistics can elevate visibility in generative responses by 65.5%. Specifically, adding clear statistics can increase visibility by 30%.
- Incorporating expert citations can increase visibility by 41%.
- These impactful statistics suggest that generative AIs place extremely high value on verifiable, data-backed, and authoritative information. This goes beyond mere “quality” in SEO to embrace a demonstrable, evidence-based approach.
Content strategies for GEO must prioritize rigorous research, expert validation, and transparent data presentation. This could involve investing more in original research, collaborating with industry experts, and meticulously citing all sources.
The emphasis shifts from persuasive writing to factual accuracy and demonstrable expertise, as AI models are designed to synthesize reliable information.
- Building authority and credibility (EEAT): Establishing strong brand authority can increase visibility in generative responses by 89.1%.A persuasive tone is not enough; inherent credibility in claims is vital. LLMs tend to extract information from domains that possess high perceived authority.
Content must be intrinsically “trustworthy” to be considered by AI models. This is achieved through online reputation, the quality of links from other web pages, and demonstrating expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness (EEAT). - Optimizing fluency and using relevant technical terminology: Text fluency optimization has been identified as one of the highest-performing strategies for GEO efforts.
Clear and natural language not only helps models process content but also makes it more appealing to readers. Precise use of domain-specific technical terms can increase visibility by 21%, especially in technical or highly specialized sectors. - Structured content: Content structuring is fundamental to facilitate analysis by AI models.
- Creating comparison tables for features and attributes, developing numbered processes for sequential steps, and implementing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) sections with schema markup are highly effective tactics.
- Including executive summaries and “TL;DR” (Too Long; Didn’t Read) sections facilitates quick content digestion by AI models.
- Structuring content with a clear and logical heading hierarchy is fundamental for AI comprehension.
- AI results with the highest success rate are those presented in simple, user-friendly formats, such as tables and lists.
- GEO strategies strongly recommend “structured content” like comparison tables, numbered processes, and FAQ sections, and note that “AI results with the highest success rate are those delivered in simple, user-friendly formats, precisely, like tables and lists”.
This is not just about human readability; it’s about optimizing for machine analysis. AI models can extract and synthesize information more easily from discrete, well-organized data points. Content creation processes must incorporate structured data formats and clear content segmentation from the outset.
This could involve using specific Content Management System (CMS) features, more rigorous implementation of schema markup, and training content creators to think in terms of “answer blocks” or “data points” rather than just flowing prose. This structural optimization directly facilitates AI’s ability to efficiently extract and present information.
- Focus on AI search intent: AIs are designed to answer a wide range of questions, including “What is [topic]?”, “Who invented [concept]?”, “Why is [thing] important?”, “How does [system] work?”, “Examples of [practice]”, “Learn [topic] step-by-step”. They are also crucial for decision-stage queries (“Best [tool] for [use case]”, “Comparison of [platforms]”) and purchase-phase queries (“Buy [product] online”, “Prices for [solution]”).
4. Differences and similitudes: SEO, LLMO, and GEO in perspective
The emergence of AI in the search landscape has sparked a debate about whether LLMO and GEO are truly new concepts or merely a “rebranding” of traditional SEO.
While there is considerable overlap in best practices, the differences in objectives and success metrics justify their distinction.
The debate: New concepts or rebranding?
Some experts, like Ahrefs, argue that LLM optimization (LLMO), generative engine optimization (GEO), and answer engine optimization (AEO) are, in essence, the same as SEO.
They contend that strategies improving visibility in traditional search engines also improve visibility in LLMs, making GEO a byproduct of SEO that does not require dedicated or independent effort.
The central argument for improving visibility in LLMs boils down to a fundamental SEO principle: creating relevant content on topics the brand wants to be associated with, both on and off its website.
However, others argue that, although they share common ground, they are not the same and have different, albeit complementary, approaches. The key lies in the nuances of how LLMs and generative engines operate compared to traditional search engines.
Key differences between SEO, LLMO, and GEO
Despite the overlap, there are fundamental differences in their objectives, strategies, and metrics:
- Primary goal:
- SEO: Its main goal is to rank web pages in the top search engine results (SERPs) to generate clicks and drive organic traffic to the website.
- LLMO: Focuses on optimizing content for large language models (LLMs) to understand, process, and effectively use it as an information source. Its goal is for the brand to be cited or included in AI-generated responses, not necessarily to generate a direct click.
- GEO: Aims for content to be cited in AI-generated responses, such as Google’s “AI Overviews” or Perplexity’s answers. The goal is for content to be selected as a source for direct AI responses, which implies visibility occurring “off-site”.
- Success metrics:
- SEO: Measured by SERP rankings, organic traffic volume, on-site conversions, and lead/sales generation.
- LLMO/GEO: Key metrics include the frequency and prominence of citations in AI responses, AI visibility score, frequency of brand mentions by reliable sources on AI platforms, and the value of “zero-click search”.. The aim is for the brand to be a recognized and reliable source for AIs.
- Content strategies:
- SEO: Focuses on keyword research, optimizing titles and meta descriptions, creating high-quality content, and link building. Relevance to search intent is crucial.
- LLMO/GEO: Prioritizes content clarity, conciseness, and directness, with a strong emphasis on semantic understanding and natural language. Question-answer formats, FAQ sections, executive summaries, lists, and tables are favored. The inclusion of citations, statistics, and real-world examples is fundamental for credibility.
- Authority building:
- SEO: Heavily relies on backlinks from high-authority websites, which act as “votes of confidence”.
- LLMO/GEO: While backlinks remain important for overall visibility, unlinked brand mentions have a much greater impact. LLMs “learn” that a brand is relevant and authoritative through the prevalence and co-occurrence of terms, and the context in which mentions are used.
Credibility in claims and presence in relevant communities are vital. LLMs tend to extract information from highly authoritative domains.
- Technical considerations:
- SEO: Includes page speed optimization (Core Web Vitals), mobile adaptability, URL structure, robots.txt and XML sitemaps, and HTTPS protocol. Google’s crawlers render JavaScript.
- LLMO/GEO: In addition to SEO’s technical considerations, it’s crucial to note that most AI crawlers (such as those from OpenAI and Anthropic) do not render JavaScript. This means that content dynamically loaded via JavaScript might not be visible to them.
The emergence of specific crawling rules for LLMs (likellms.txt) is anticipated to guide these tools through content.
Comparison table: SEO vs. LLMO vs. GEO
| Characteristic | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
| Primary goal | Increase visibility and organic traffic through SERP rankings. | Optimize content for LLMs to understand, use, and cite in their responses. | Get content cited in direct AI responses (AI Overviews, chatbots). |
| Success metric | Rankings, organic traffic, clicks, on-site conversions. | Frequency and prominence of citations in AI responses, AI-perceived authority. | Citation frequency, AI visibility score, zero-click value, brand mentions. |
| User journey | Direct user to website to consume content. | Influence information LLM presents to user, often without clicking to site. | Provide direct answer to user, reducing need to visit site. |
| Content focus | Keywords, quality content, meta tags, heading structure. | Semantic clarity, natural language, Q&A format, informational depth. | Accuracy, comprehensiveness, expert citations, statistics, structured content (tables, lists). |
| Authority | Quality backlinks, online reputation, brand mentions. | Unlinked brand mentions, prevalence in training data, credibility of claims. | Demonstrable credibility, cited sources, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (EEAT). |
| Technical considerations | Load speed, mobile optimization, crawling/indexing, HTTPS, sitemaps, robots.txt. | Accessibility for crawlers that don’t render JavaScript, llms.txt (future). | Similar to LLMO, with emphasis on structure for easy data extraction. |
| Search intent | Informational, navigational, commercial, transactional (directing to page). | Understand underlying intent to generate direct, useful answers. | Answer “what,” “how,” “why,” “best,” “comparison” questions directly. |
| Natur | Long-term, continuous process, fundamental for online visibility. | Adaptation to AI evolution, emerging competitive advantage. | Innovative strategy for the new era of generative engines. |
Overlaps and nuances
The overlap between SEO, LLMO, and GEO is undeniable. The foundation of all three is the creation of high-quality, relevant, and authoritative content. Content well-structured for LLMO is often also clearer and more semantic, which can improve traditional SEO.
In fact, good SEO ranking increases visibility in LLMs, and at the same time, LLM models that display updated information can increase traffic and, consequently, improve SEO.
However, the nuances are important. While SEO focuses on visibility in search results to generate clicks, LLMO and GEO focus on being the direct information source for AI responses, often resulting in “zero-click search”.
The importance of unlinked brand mentions for LLMO/GEO is a key difference from SEO, where backlinks are paramount for authority. Furthermore, AI crawlers’ sensitivity to JavaScript presents a specific technical challenge for LLMO/GEO that is not as critical for traditional SEO.
Ultimately, most strategies that benefit LLMO and GEO (clear, concise, structured, authoritative content, with citations and statistics) are extensions of SEO best practices that already focus on search intent and user content quality. The difference lies in the intensity of applying these practices and the ultimate goal of visibility.
5. The perfect synergy: Integrating SEO, LLMO, and GEO
In today’s dynamic digital landscape, optimization for search engines, language models, and generative engines are not isolated disciplines, but interconnected components of a holistic online visibility strategy.
The key to success lies in understanding how they complement each other and how they can be integrated to maximize a brand’s presence across all search and discovery channels.
A Holistic and complementary approach
GEO and LLMO do not replace traditional SEO; rather, they act as complementary tools that enhance the overall digital marketing strategy.
By combining these approaches, businesses can leverage the unique strengths of each: SEO provides long-term visibility and established organic traffic, while LLMO and GEO offer direct and authoritative visibility in AI responses, adapting to new user search habits.
Integrating these strategies allows businesses to maximize their presence in search engines, capture a wider range of queries, and reach a broader audience at all stages of the buying cycle.
Content strategy integration
Content creation is the main bridge between SEO, LLMO, and GEO. Well-designed content can serve the objectives of all three:
- Conversational and question-oriented content: Creating content with a conversational tone that reflects user language and directly answers “why?” and “how?” questions is crucial.
This not only improves readability for users but also makes it easier for LLMs to extract direct answers. Using question-and-answer formats or FAQ sections with schema markup is highly effective for this. - Semantic focus and depth: Instead of focusing solely on keyword density, the strategy should emphasize semantic keywords and natural language, covering topics comprehensively and in depth. LLMs value contextual integrity and complete coverage of a topic.
Creating comprehensive and detailed content, providing rich context and concrete practical knowledge, is fundamental. - Structured data and schema markup: Implementing structured data (such as
FAQPage,HowTo,Articleschema) is vital. This helps AI systems understand the meaning and context of content, increasing the likelihood of it appearing as a featured snippet or a direct answer in “AI Overviews”. - Citations and evidence: Integrating expert citations, statistics, data, and real-world examples into content reinforces credibility and authority, which is highly valued by both traditional search engines (EEAT) and LLMs.
- Constant updates: Keeping content fresh and updated, removing outdated information and adding the latest statistics and trends, is crucial for relevance in LLMs and search engines.
Technical integration
While technical differences exist, technical optimization can and should be unified:
- Crawling and Indexing: Ensuring the website is crawlable and indexable by traditional search engines remains the foundation. However, it is also important to consider accessibility for AI crawlers, especially those that do not render JavaScript. This may require ensuring critical content is available in the initial HTML or through server-side rendering.
- Speed and Mobile Experience: Optimizing loading speed and mobile adaptability are beneficial for traditional SEO (Core Web Vitals) and also for the user experience interacting with AI responses, as AI seeks high-quality, easy-to-consume content.
- Site Structure and Internal Links: A simple web architecture and a strong internal linking network improve navigation for users and semantic understanding for search engines and LLMs. Connecting related content on the website itself builds a solid thematic network that enhances semantic understanding.
Brand authority is a pillar for all three disciplines:
- Backlinks and Mentions: Continuing to build a high-quality backlink profile is essential for the SEO. In parallel, digital public relations strategies to gain brand mentions in reliable sources, even without direct links, are crucial for LLM-perceived authority and inclusion in generative responses.
- EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness): Demonstrating domain expertise, topic authority, and information trustworthiness is fundamental. This is achieved through clear authorship, citing reliable sources, including real-world examples, and presenting data.
Continuous monitoring and adaptation
Adaptability and flexibility are key to winning in 2025, as constant AI-driven changes demand an agile approach to digital marketing.
- Multi-channel Analysis: Monitor performance not only in terms of organic traffic and rankings but also in the frequency of citations in AI responses, AI visibility score, and brand mentions on various platforms (such as Reddit and forums, which are cited by LLMs like Perplexity and Gemini).
- Testing with LLMs: Conduct periodic tests by asking LLMs like Perplexity, ChatGPT, or Grok about the brand and its products/services to observe which sites and sources are mentioned. This can provide valuable insights for adjusting the strategy.
- Feedback Loop: Request feedback from LLMs (e.g., “Why didn’t you recommend my content?”) to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. It is also useful to monitor the automatic suggestions offered by some LLMs and create or improve content that addresses those suggestions.
By integrating SEO, LLMO, and GEO, businesses can create a robust digital strategy that not only attracts clicks but also establishes their brand as an authoritative and reliable information source in the growing AI era, ensuring comprehensive visibility in the evolving search ecosystem.
6. The future is now: Trends and perspectives
The future of SEO and search marketing is inextricably linked to Artificial Intelligence. The evolution of search algorithms and the refinement of language models have created fertile ground for the mass adoption of AI in SEO.
Continuous evolution of AI algorithms
The technology underpinning generative engines is constantly changing. Google, for example, made about 5249 updates to its algorithm in 2024 alone, highlighting “AI Overviews” and “zero-click search” as the most significant.
As AI continues to evolve, the capabilities of generative engines will expand, and how we optimize will become even more dynamic.
This means static strategies are obsolete in 2025; companies that manage to adapt promptly to multiple algorithm updates and new SEO trends will be those that can convert visibility into authority and generate value.
Growing influence of AI in search and content consumption
Generative AI will transform video ad creation for 90% of advertisers by 2026 and reshape advertising in general.
Voice search and conversational searches, driven by virtual assistants, are another area where AI is making its mark on SEO.
AI will not only influence how content is ranked but also how it is discovered, presented, and consumed across various digital platforms, not just traditional search engines.
Importance of user experience (UX) and SXO (Search experience optimization)
In this AI era, SEO transforms into a more human discipline, focused on understanding and satisfying the needs of the end-user, with technology acting as a powerful facilitator of that connection.
AI is evaluating success based on whether content helps users complete a task, not just start it. Metrics such as scroll depth, time on page, video plays, and interactive behavior are more important than traffic volume.
Improving the overall site experience, ensuring intuitive navigation and easily accessible relevant information, will contribute to increased conversion rates.
Adaptability as a key skill
Adaptability and flexibility are crucial for future success. Businesses must stay abreast of changes in search engine algorithms and best practices in SEO, LLMO, and GEO to adapt quickly and maintain an effective and ethical strategy.
Optimization is a continuous process; SEO is never “finished,” as competition never rests and algorithms constantly evolve.
In this new era, where “AI Overviews” and zero-click search dominate results, it’s crucial to create content for people, but package it for AI. The key is no longer to attract clicks, but to ensure your brand is the trusted source AI chooses to recommend, even when conversion happens directly on Google.
7. Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Below are some of the most common questions about SEO, LLMO, and GEO, providing clarity on these evolving concepts.
What exactly is SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the strategic process of improving a website’s visibility and ranking in the organic results pages of search engines like Google and Bing.
Its goal is to increase qualified traffic and online presence without resorting to paid advertising. It involves optimizing content, the site’s technical structure, and external authority.
What is LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization)?
LLMO is the optimization of web content so that it can be interpreted, cited, and used by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini.
It does not aim to rank you in traditional search engines, but in AI-generated responses, making your content a recognized source for these artificial intelligences.
What is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
GEO is a digital strategy that seeks to enhance content visibility and influence within responses generated by AI-powered platforms, such as Google’s “AI Overviews” or Perplexity’s answers.
Its goal is for content to be recognized and used by LLMs when formulating direct answers to user queries, often without requiring a click to the website.
How does LLMO differ from traditional SEO?
The main difference lies in the objective. Traditional SEO aims to rank on Google to get clicks and direct traffic.
LLMO, on the other hand, seeks for your content to be understood and chosen as a source by language models, which operate with different criteria and generate direct responses, potentially resulting in “zero-click search”.
LLMO addresses aspects such as semantics, content structure, informational depth, and AI-perceived authority, beyond just keywords.
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
GEO differs from SEO in that it does not just aim to improve SERP rankings, but for content to be cited directly in AI-generated responses.
While SEO seeks to attract clicks to your website, GEO aims for your brand to appear directly in AI-synthesized responses.
GEO emphasizes content accuracy, the inclusion of citations and statistics, and building authority to be considered a reliable source by generative engines.
Are LLMO, GEO, and SEO the same or different?
They are not the same, but they are complementary and share common ground.
While LLMO and GEO are often used interchangeably to refer to optimization for generative AI, they have nuances. SEO is the foundation for search engine visibility. LLMO focuses on content comprehension by language models, while GEO focuses on being cited in direct responses from generative engines. The strategies of all three should be worked on together to achieve more effective results.
Can GEO replace traditional SEO methods?
No, GEO is not a complete replacement for traditional SEO. It should be seen as a complementary tool that enhances the overall SEO strategy. Combining GEO with traditional SEO techniques can lead to better results and more comprehensive visibility in the digital ecosystem.
What type of content is optimized with LLMO and GEO?
Any informational content that a language model can interpret as useful for answering a query can be optimized. This includes product pages, FAQs, technical texts, blog articles, guides, case studies, and content that answers “how” or “why” questions.
Content must be comprehensive, accurate, and well-structured.
How do language models work with my website?
Language models extract, summarize, or reference content from multiple sites to generate responses. If your content is not clear, deep, or trustworthy, they will ignore it.
They use content to understand user intent and synthesize the most relevant information.
Can I apply LLMO to existing content?
Yes, in fact, content well-structured for LLMO tends to be clearer and more semantic, which can improve your existing SEO.
It is recommended to audit current content to identify improvement opportunities, rewrite with AI in mind (more clarity, less “fluff”), and add FAQ sections.
Does Google penalize websites with AI-generated content?
Google focuses on content quality and relevance, not how it was created. Websites with AI-generated content will not be penalized as long as the content is valuable, original, and provides a good user experience. However, it is crucial to ensure that the content complies with Google’s quality guidelines and is not perceived as spam or low-quality.
Google has already started penalizing low-quality AI-generated content.
What concrete benefits can I expect from LLMO and GEO?
Increased brand visibility, a boost in perceived authority, new traffic sources (even without direct clicks), and significant differentiation from the competition.
By being present in AI-generated responses and summaries, businesses can establish themselves as thought leaders in their fields.
How can I start implementing LLMO and GEO?
Implementing LLMO and GEO requires a combination of AI technology and SEO expertise. It is essential to focus on context and conversational content, emphasize semantic keywords and natural language, implement structured data, create comprehensive and in-depth content, optimize metadata and internal links, and build strong digital authority.
It is also crucial to monitor LLM results and adjust the strategy based on data.
What does “zero-click search” mean and how does it affect ranking?
“Zero-click search” occurs when users get the desired answer directly on the search engine results page (e.g., via an “AI Overview”) without needing to click on any link.
This means brand visibility can now occur “off-site”. The impact is that success metrics expand beyond direct traffic, including citation frequency and brand visibility in AI responses.
What is the role of original content in the context of GEO?
Original content remains essential. Although AI can generate content, generative engines value content that provides unique value, exclusive data, original research, case studies, and expert perspectives that AI cannot easily replicate.
High-quality, original content is fundamental for building authority and being cited by AI.
Conclusions and tips
The Artificial Intelligence era has fundamentally redefined the digital visibility landscape. What was once a singular focus on traditional SEO has now expanded to include Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
Understanding these three disciplines, their differences, and, crucially, their synergies, is indispensable for any forward-thinking digital marketing strategy.
The analysis of search evolution reveals an undeniable shift from a click-based model to one where direct delivery of answers by AI is increasingly prevalent.
This demands a re-evaluation of success metrics, where brand citation frequency and AI-perceived authority become as important as rankings and organic traffic.
Content quality, accuracy, and structure are the pillars supporting effectiveness across all three domains, but with an intensity and focus adapted to each’s particularities.
To thrive in this new ecosystem, adopting a unified and adaptive digital visibility strategy is recommended:
- Prioritize content quality and depth: Invest in creating comprehensive, accurate, and data-driven content. This includes incorporating statistics, expert citations, and real-world examples to reinforce credibility and authority, elements highly valued by LLMs and generative engines.
- Optimize for AI comprehension: Structure content so it is easily digestible by AI algorithms. This implies the extensive use of question-and-answer formats, FAQ sections, lists, tables, and concise summaries. Implementing structured data (Schema Markup) is fundamental for signaling content meaning and context to AI.
- Build holistic brand authority: Beyond traditional backlinks, it is crucial to foster unlinked brand mentions in reliable sources and establish the brand’s expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness (EEAT) in its domain. The goal is to become a recognized and authoritative entity in the digital ecosystem.
- Consider AI-specific technical implications: Pay attention to how AI crawlers interact with the website, especially regarding JavaScript. Ensuring critical content is accessible to all types of crawlers is vital for visibility.
- Adopt a continuous monitoring and agile adaptation approach: The AI landscape is constantly evolving. Businesses must actively monitor their visibility in traditional and generative search results, conduct tests with LLMs, and be prepared to continuously adapt their content strategies and optimization techniques.
In summary, while SEO remains the foundation, LLMO and GEO represent the necessary evolution to ensure a complete digital presence in the AI era.
The intelligent integration of these disciplines is not an option, but a strategic imperative for any brand aspiring to maintain its relevance and achieve success in the future of digital marketing.